In today’s interconnected world, the concept of global power extends beyond military strength to encompass economic influence, technological prowess, diplomatic leverage, and cultural impact. As nations vie for dominance on the world stage, understanding who holds the mantle of the most powerful country requires a nuanced analysis of multiple factors. Let’s delve into the intricate web of metrics that define global power and attempt to discern which country currently reigns supreme.

Military Strength:
Military prowess remains a cornerstone of global power. The ability to project force, deter aggression, and respond swiftly to threats shapes international dynamics. The United States consistently ranks at the forefront due to its unparalleled military budget, technological innovation, and global military presence. With a vast nuclear arsenal, advanced weaponry, and extensive military alliances, the U.S. sets the benchmark for military capabilities.
Following closely, Russia maintains a formidable military force, particularly potent in strategic areas such as cyber warfare, missile technology, and Arctic defense. China, rapidly modernizing its military with substantial investments in naval capabilities, missile systems, and cyber capabilities, also asserts itself as a major player in global military power.
Economic Influence:
Economic strength underpins geopolitical influence. The United States leads in nominal GDP, supported by a diverse economy, technological innovation hubs, and global financial institutions headquartered on its soil. Its currency, the U.S. dollar, serves as the world’s primary reserve currency, further bolstering its economic clout.
China, propelled by decades of rapid industrialization and infrastructure development, has emerged as a global economic powerhouse. With the world’s largest population and significant investments in technology, manufacturing, and international trade initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, China’s economic influence continues to expand.
Technological Innovation:
In the digital age, technological advancement is a crucial determinant of power. The United States maintains an edge in innovation hubs such as Silicon Valley, fostering breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and cybersecurity. Its tech giants wield immense influence globally, shaping trends in consumer technology and digital infrastructure.
China, investing heavily in emerging technologies like 5G, quantum computing, and space exploration, aims to lead in critical technological domains. Russia, known for its prowess in aerospace engineering, cybersecurity capabilities, and defense technologies, also remains a formidable force in technological innovation.
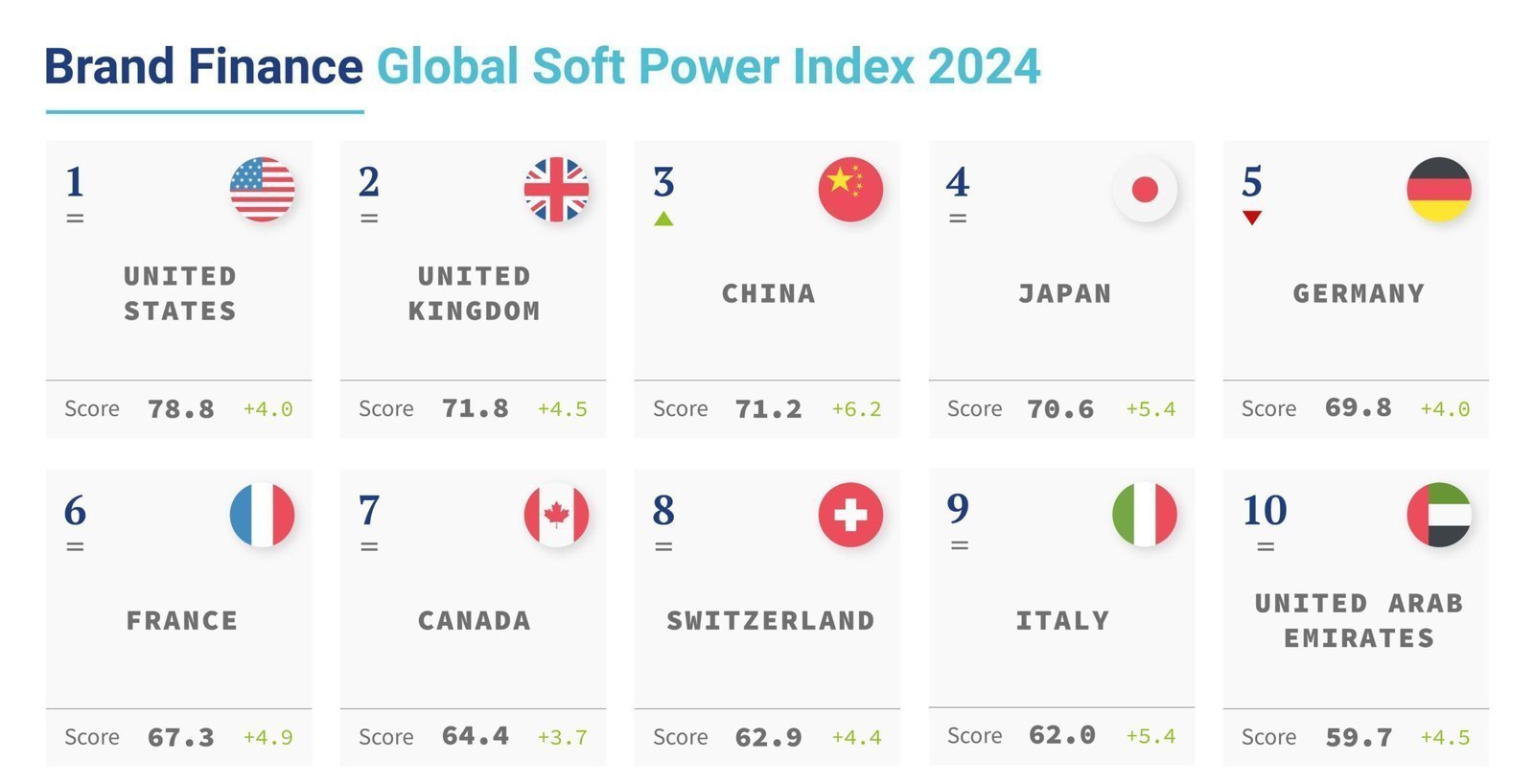
Diplomatic and Soft Power:
Soft power, derived from cultural influence, diplomatic acumen, and global alliances, plays a pivotal role in shaping perceptions and policies worldwide. The United States leverages its cultural exports, educational institutions, and global networks to propagate its values and policies. Its alliances, such as NATO, and diplomatic engagements reinforce its leadership position.
China employs soft power through initiatives like Confucius Institutes, international media outlets like CGTN, and strategic investments in cultural diplomacy. Russia, meanwhile, uses its cultural heritage, energy resources, and diplomatic maneuvers to influence global discourse and policy decisions.
Geopolitical Strategy and Influence:
Geopolitical strategy encompasses a nation’s ability to navigate regional conflicts, forge alliances, and shape international norms. The United States, with a network of military alliances and strategic partnerships across Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Middle East, exercises considerable influence in global security architecture.
China’s Belt and Road Initiative and assertive territorial claims in the South China Sea underscore its ambition to reshape regional dynamics and expand its sphere of influence. Russia, adept at leveraging energy resources and geopolitical alliances, seeks to maintain influence in its immediate neighborhood and beyond.
Conclusion:
Determining which country reigns supreme in global power rankings necessitates a comprehensive evaluation of military strength, economic influence, technological innovation, soft power, and geopolitical strategy. While the United States remains a preeminent global power across multiple domains, China’s rapid ascent and Russia’s strategic maneuvers pose significant challenges to the existing geopolitical order.
As dynamics shift in an increasingly multipolar world, the interplay of these factors will continue to define global power dynamics. The quest for supremacy is not just about military might or economic prowess but also about adaptability, innovation, and strategic foresight in an ever-evolving geopolitical landscape.